The Science of Lightning
Why do we get lightning?
When you rub your hands together quickly, they get hot. This is due to a force called friction. Friction is the resistance that occurs when multiple surfaces rub against each other, slowing down movement and creating heat.
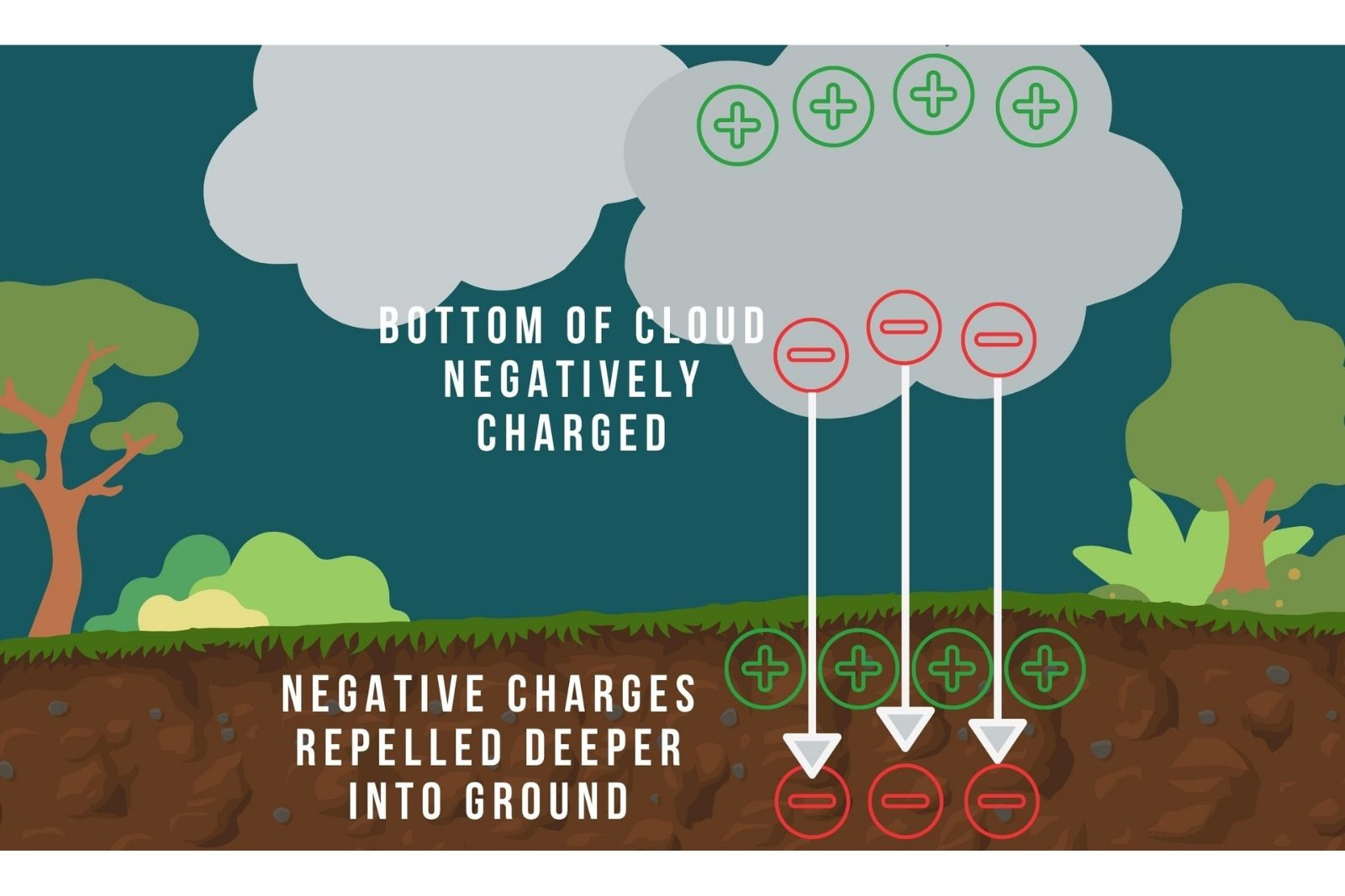
Friction also occurs in thunder clouds – air currents cause water and ice to move around in the clouds causing water molecules to bump into each other – to collide – generating friction and causing tiny particles called electrons to get knocked out of the molecules. These electrons are negatively charged and fall to the bottom of the cloud creating static electricity.
These negative charges repel the negative charges found on the ground below deeper into the earth leaving the ground surface positively charged. Once a significant charge separation has built up between the cloud and ground, the charges seek to equal each other out and neutralise.
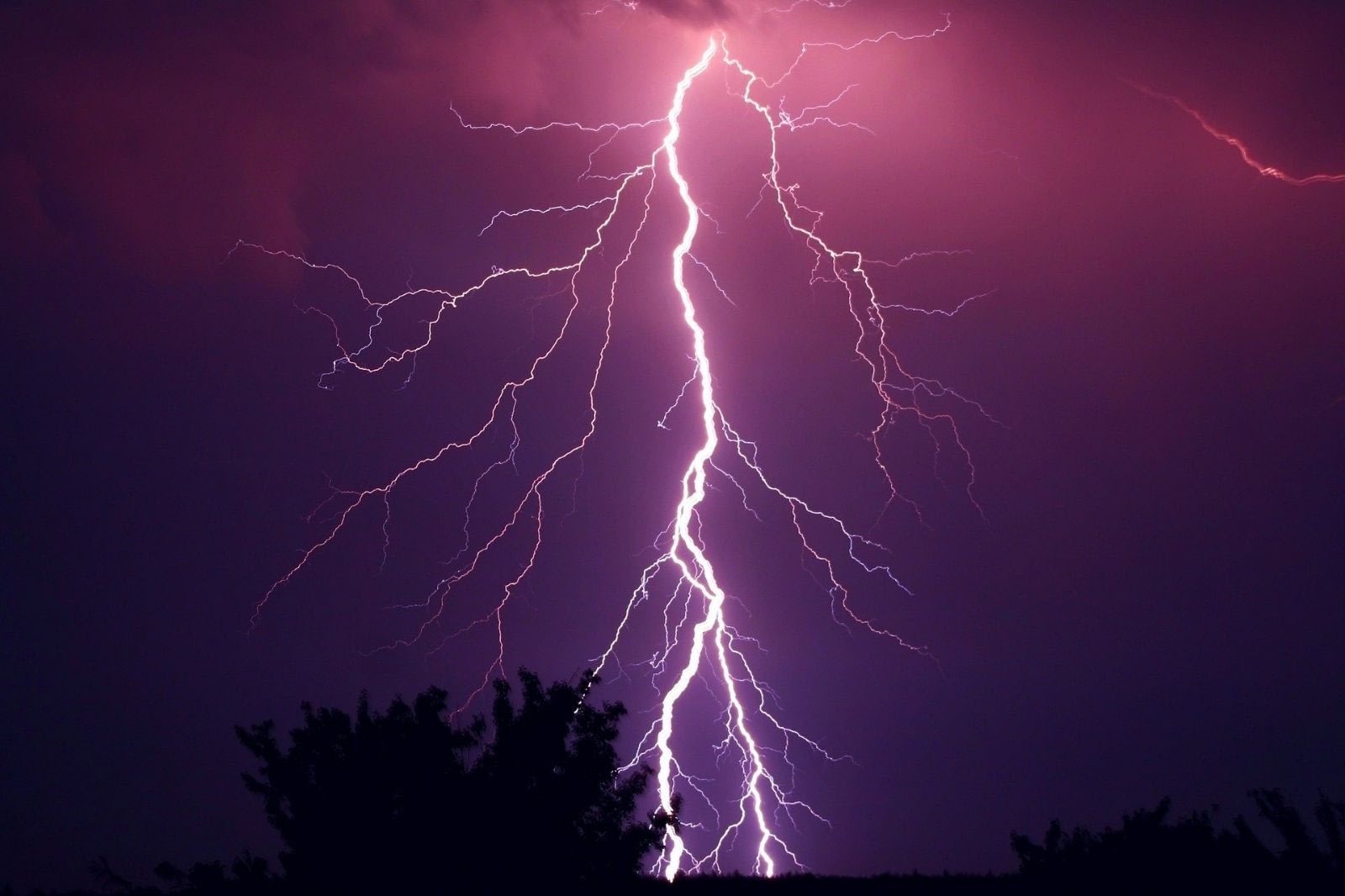
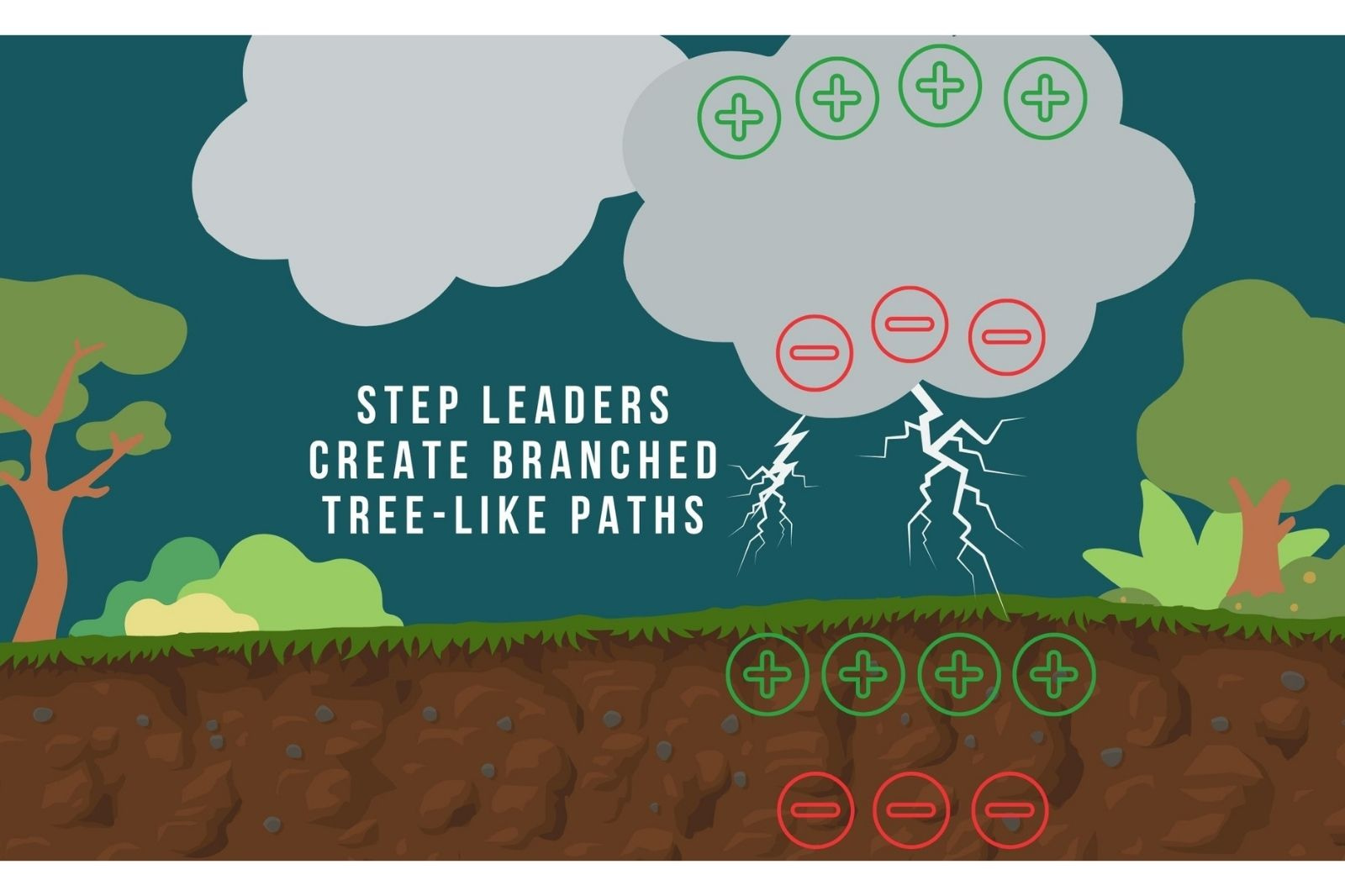
Paths of charged air, called step leaders, are produced from the charged clouds at a speed of 200,000 miles per hour and appear as branched tree-like patterns of bright light.
The first step leader to reach the ground creates the conductive path for the following bright strike of lightning to flow all the way down. If you watch carefully, this can be seen in the slow motion video below.
How to make your own charged cloud
You will need...
- Metal drinks can
- Balloon
- Soft cloth
Ensure your drinks can is empty and clean.
- Blow up your balloon and tie it at the bottom
- Rub the balloon against the soft cloth
- Then quickly turn the drinks can on its side on a flat, hard surface and hold the balloon near the can but without touching it
- You should be able to move the balloon along in front of the can while the can follows behind it
When you rub the balloon, friction causes electrons to come off the soft cloth and transfer to the balloon’s surface making it negatively charged. When you put the balloon close to the can, its negative electrons are repelled away from the can’s surface by the electrons on the balloon’s surface but its positive charges are attracted to the balloon’s negative charges so follows the balloon when it moves. This is an example of static electricity.
Bonus Experiment!
This video below shows another experiment using static electricity to separate a mixture of salt and pepper, watch to find out how!
- You can find out roughly how far away a storm is by counting how long the gap is between seeing lightning and hearing thunder due to the different speeds at which light and sound travel. Light at 300 million metres per second and sound only 300 metres per second. Therefore, for every 4 second period between a lightning flash and its thunder rumble, the thunderstorm is 1 mile away.
- At any one time there are over 2,000 thunderstorms occurring worldwide, each producing over 100 lightning strikes per second. You can view a live map of lightning strikes in the UK here.
- This means over 8 million lightning bolts of produced worldwide every day.
- Each lightning flash is approximately 3 miles long but only roughly a sing centimetre in width.
- On average a lightning flash discharges between 1-10 billion joules of energy and a current of 30,000-50,000 amps.